The Esprit OMI/HIC![]() project has developed two bi-directional serial link technologies
which form the basis of the IEEE 1355 standard :
project has developed two bi-directional serial link technologies
which form the basis of the IEEE 1355 standard :
The work reported here is based on the DS link technology. The bit-level
encoding is shown in Figure 1. The data line carries the binary data
values and the strobe line only changes state when a data bit has
the same value as the previous one. This scheme allows for a full
bit period of skew tolerance. It also means that the links are asynchronous,
as the data/strobe signal pair carries an encoded clock. Studies on
the reliability of DS links [6], up to distances of 20 meters,
have measured a bit error rate of better than ![]() .
.
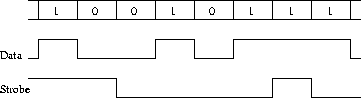
Figure 1: DS-Link bit level protocol
The IEEE 1355 protocol stack defines another three protocol layers above the bit layer: the character, exchange and packet layers. Characters are a groups of consecutive bits which represent data or control information. The exchange layer controls the exchange of characters in order to ensure the proper functioning of a link. It includes functions such as link flow control and the link startup mechanism. DS links use a credit based flow control scheme which operates on a per link basis. This ensures that the switching fabric is lossless : no characters will be lost due to internal buffer overflow.
Information in a DS link network is transferred in packets. A packet consists of a header, which contains the routing information, a payload of zero or more data bytes and an end of packet marker. The protocol allows arbitrary length packets to be sent.